Revolutionizing Architecture: A Comprehensive Guide to Integrate Virtual Reality in Architectural
The art of persuasion is a significant challenge in the field of architecture. At Green Hat Studio, we emphasize the importance of convincing clients about the outcome of a space, ensuring them that their dreams are in capable hands, and assuring them that the designs will exceed expectations. Successfully conveying creative ideas to clients has long been a challenge, but the evolution of technology, specifically Virtual Reality (VR), has effectively addressed this communication gap. In the realm of architecture, VR has emerged as an innovative and interactive tool, transforming the design and presentation process. This technology introduces exciting possibilities for architects, designers, and students alike, influencing architecture across different stages, including design conceptualization, development, monitoring, and presentations.
VR has become a game-changer in architecture, offering an immersive experience that enhances the visualization of spaces long before they are built. It not only creates an experience but also provides a realistic feel for how a space will be in reality. While some firms have embraced this technology, others are still experimenting or unsure about where to begin. This blog aims to explore the implementation of VR in architectural firms, shedding light on the advantages, challenges, and steps to seamlessly integrate this cutting-edge technology.
Getting Started with VR Implementation
Implementing virtual reality is more than just purchasing VR headsets; it requires intuitive, hassle-free software to unlock its creative potential. As this field continues to evolve, many companies are developing programs that aim to become industry standards in the future. Fortunately, there are already user-friendly software options that can generate VR models, ranging from basic to realistic experiences. Here are some easy-to-use software options that architects can leverage:
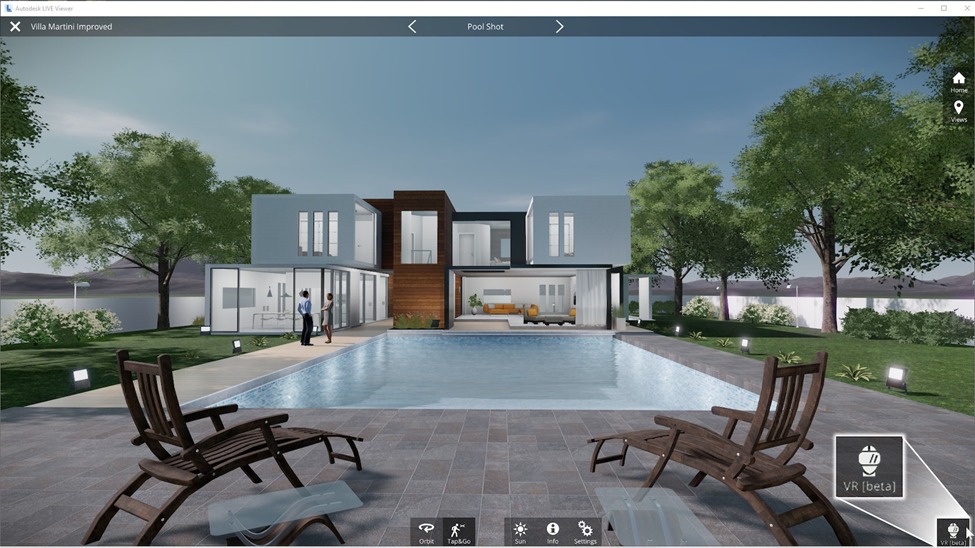
Autodesk Live
Autodesk LIVE allows users to transform Revit models and step inside their own designs to share and present. Launched in July 2016, it has since added virtual reality functionality. AEC professionals can upload BIM models to the cloud with just one click, and interactive visualizations can be published to mobile. This gives clients a better sense of your design early on so changes can be made with minimal disruption or delay.
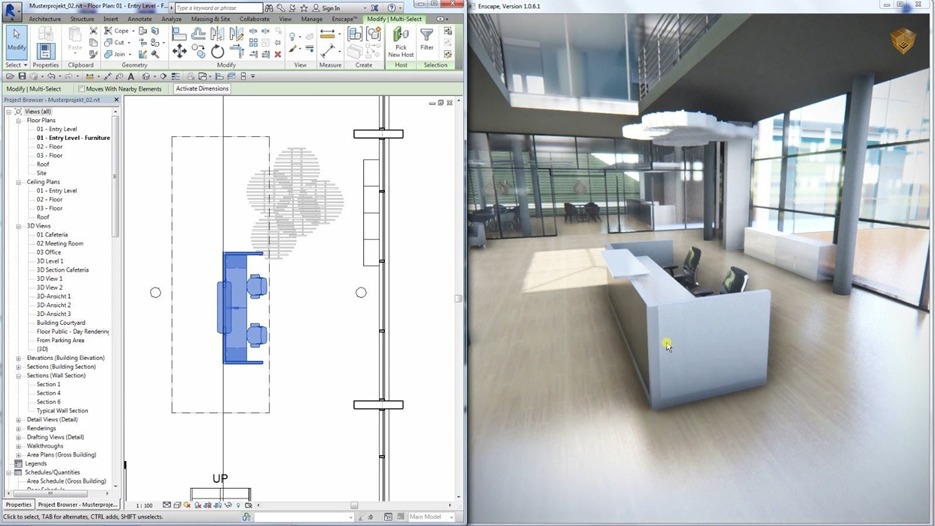
Enscape:
Enscape is a Revit/Sketchup plug-in that creates a VR walk-through with one click based on your BIM data. There is no need to download or learn how to operate additional software. All materials, geometry, and entourage come from your Revit project and can be changed during the VR simulation. This flexibility allows spontaneous presentations with the real-time rendering quality within the architectural design workflow. Combined with the Oculus Rift, customers can virtually walk through your Enscape project and experience it as if it were already built.
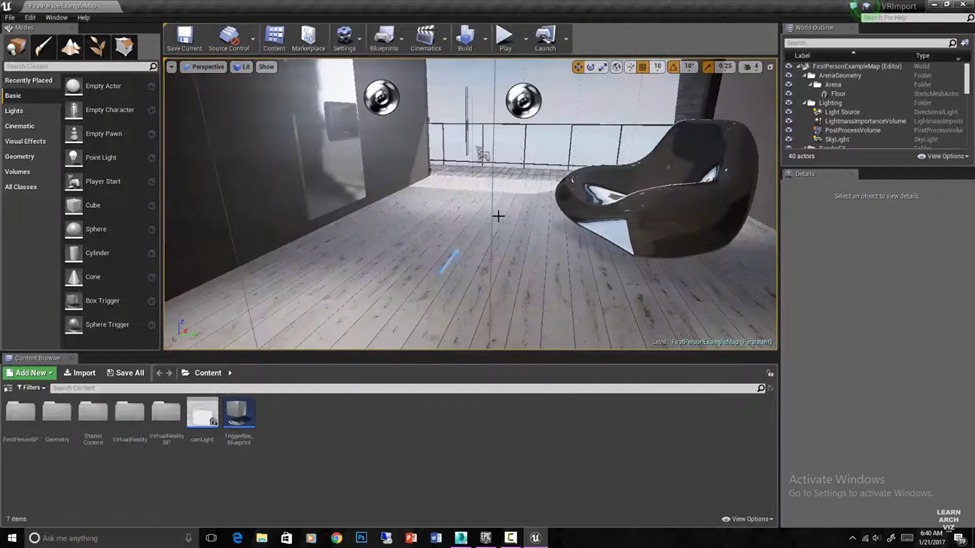
Unreal Engine:
Unreal Engine Unreal is a suite of tools for developers that can be used to create games and virtual reality environments. It is free for the architecture industry and is frequently used to visualize spaces and render architectural models in immersive environments. This tool enables engineers and architects to design and build in a virtual reality environment by means of a powerful editor tool-set and the interaction models that have been specifically designed for VR world-building. The outcome is a believable immersive experience built upon natural motions and interactions. It is supported by Oculus, Steam VR, Samsung gear, Google daydream, Microsoft mixed reality HMDs.
Beyond the previously mentioned software, other options provide even more versatility for VR experiences:
– Unity: While primarily a game engine, Unity does offer VR capabilities, but it requires programming skills to create interactive VR environments. Those seeking more focused VR development platforms might consider Blender or VRChat.
– Lumion: While Lumion doesn’t directly connect to PC-based VR headsets, it excels in generating immersive 360-degree panoramas. These panoramas can be viewed effectively in VR using platforms like SentioVR. For alternative VR panorama creation tools, explore Marzipano or Krpano.
Choosing the Right VR Headset
Choosing a VR headset involves considering a variety of brands, including wireless, PC-tethered, and smartphone-based options, with prices ranging from Rs. 9,000 to Rs. 100,000. Each brand has its pros and cons:
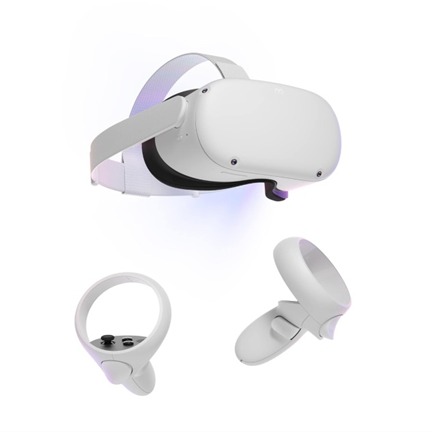
Oculus Quest 2: The Oculus Quest 2 is a standalone VR headset that does not require a PC to operate. It features a high-resolution display, a wide field of view, and accurate tracking. It also has a number of built-in features, such as 3D spatial audio and hand tracking. It is supported by any software; it just requires the panoramas or the VR models to be exported into the device.
Oculus Rift S: The Oculus Rift is the head-mounted display (HMD) that is currently supported by Enscape. The Oculus is one of the first and most widely used HMDs worldwide. The final version runs with a resolution of 2160×1200 pixels. This is the preferred Enscape solution as it runs in similar quality as the Vive at a lower price.
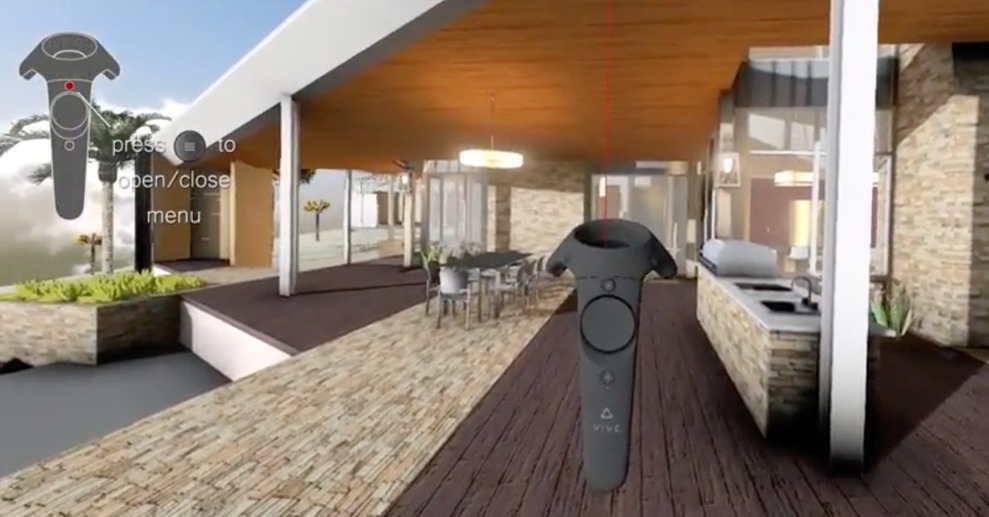
HTC Vive: The HTC Vive is also supported in Enscape. The resolution of the screens is comparable to the Oculus Rift. The Vive comes with great positional tracking, meaning that the user can move naturally in an area of 15 feet by 15 feet (5 m × 5 m). This is a great advantage and at the same time a disadvantage as it needs to be installed in a certain area to get the most out of this technology.
How to Choose the Right VR Headset
Determining your needs, budget, and computer compatibility is crucial before choosing a VR headset. Whether it’s for viewing 3D models or experiencing 360-degree walkthroughs, understanding your specific requirements will help narrow down options. Consider your budget for the best experience, keeping in mind that VR headsets require powerful gaming PCs for proper functioning. Other technical aspects to consider include display quality, field of view, tracking, controllers, and comfort.
Cost of Implementing VR at Architectural Firms
The implementation cost depends on the chosen software and hardware. Initial investments typically involve one or two VR headsets for reviewing client satisfaction and internal workflow. Monthly or yearly subscriptions for software, ranging from Rs. 2,000 to Rs. 4,000, can be discontinued at any point. The cost of hardware, including VR headsets, ranges from Rs. 9,000 to Rs. 100,000.
Conclusion
Once acquainted with the necessary software and hardware, you are ready to enter the world of virtual reality, creating unique experiences for yourself and your clients. Implementing virtual reality in architectural firms is a transformative journey. Despite the challenges, the long-term benefits of improved efficiency and client satisfaction make VR a worthwhile investment. By carefully assessing needs, selecting appropriate technology, and embracing a culture of learning, architectural firms can unlock the full potential of virtual reality, stepping into an innovative future of architectural design.

Blog By Ar. Anushka Kulkarni,
Junior Architect at Green Hat Studio